pyproximal.L21#
- class pyproximal.L21(ndim, sigma=1.0)[source]#
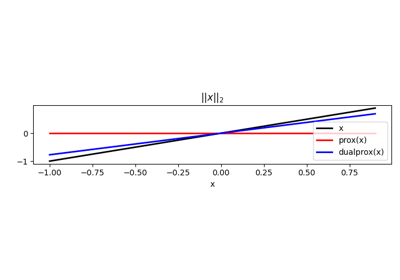
\(L_{2,1}\) proximal operator.
Proximal operator for \(L_{2,1}\) matrix norm.
- Parameters
- ndim
int Number of dimensions \(N_{dim}\). Used to reshape the input array in a matrix of size \(N_{dim} \times N'_{x}\) where \(N'_x = \frac{N_x}{N_{dim}}\). Note that the input vector
xshould be created by stacking vectors from different dimensions.- sigma
float, optional Multiplicative coefficient of \(L_{2,1}\) norm
- ndim
Notes
Given the \(L_{2,1}\) norm of a matrix of size \(N_{dim} \times N'_x\) defined as:
\[\sigma \|\mathbf{X}\|_{2,1} = \sigma \sum_{j=0}^{N'_x} \|\mathbf{x}_j\|_2 = \sigma \sum_{j=0}^{N'_x} \sqrt{\sum_{i=0}^{N_{dim}}} |x_{ij}|^2\]the proximal operator is:
\[\prox_{\tau \sigma \|\cdot\|_{2,1}}(\mathbf{x}_j) = \left(1 - \frac{\sigma \tau}{max\{||\mathbf{x}_j||_2, \sigma \tau \}}\right) \mathbf{x}_j \quad \forall j\]Similar to the Euclidean norm, the dual operator is defined as:
\[\prox^*_{\tau \sigma \||\cdot\|_{2,1}}(\mathbf{x}_j) = \frac{\sigma \mathbf{x}_j}{\max\{||\mathbf{x}_j||_2, \sigma\}} \quad \forall j\]Finally, we note that the \(L_{2,1}\) norm is a separable function on each column on the matrix \(\mathbf{X}\). Taking advantage of the property of proximal operator of separable function [1], its proximal and dual proximal operators can be interpreted as a series of
pyproximal.proximal.Euclideanoperators on each column of the matrix \(\mathbf{X}\).- 1
N., Parikh, “Proximal Algorithms”, Foundations and Trends in Optimization. 2013.
Methods
__init__(ndim[, sigma])affine_addition(v)Affine addition
chain(g)Chain
grad(x)Compute gradient
postcomposition(sigma)Postcomposition
precomposition(a, b)Precomposition
prox(**kwargs)proxdual(**kwargs)