Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Adaptive Primal-Dual#
This tutorial compares the traditional Chambolle-Pock Primal-dual algorithm with the Adaptive Primal-Dual Hybrid Gradient of Goldstein and co-authors.
By adaptively changing the step size in the primal and the dual directions, this algorithm shows faster convergence, which is of great importance for some of the problems that the Primal-Dual algorithm can solve - especially those with an expensive proximal operator.
For this example, we consider a simple denoising problem.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylops
from skimage.data import camera
import pyproximal
plt.close('all')
def callback(x, f, g, K, cost, xtrue, err):
cost.append(f(x) + g(K.matvec(x)))
err.append(np.linalg.norm(x - xtrue))
Let’s start by loading a sample image and adding some noise
We can now define a pylops.Gradient operator as well as the
different proximal operators to be passed to our solvers
# Gradient operator
sampling = 1.
Gop = pylops.Gradient(dims=(ny, nx), sampling=sampling, edge=False,
kind='forward', dtype='float64')
L = 8. / sampling ** 2 # maxeig(Gop^H Gop)
# L2 data term
lamda = .04
l2 = pyproximal.L2(b=noise_img.ravel(), sigma=lamda)
# L1 regularization (isotropic TV)
l1iso = pyproximal.L21(ndim=2)
To start, we solve our denoising problem with the original Primal-Dual algorithm
# Primal-dual
tau = 0.95 / np.sqrt(L)
mu = 0.95 / np.sqrt(L)
cost_fixed = []
err_fixed = []
iml12_fixed = \
pyproximal.optimization.primaldual.PrimalDual(l2, l1iso, Gop,
tau=tau, mu=mu, theta=1.,
x0=np.zeros_like(img.ravel()),
gfirst=False, niter=300, show=True,
callback=lambda x: callback(x, l2, l1iso,
Gop, cost_fixed,
img.ravel(),
err_fixed))
iml12_fixed = iml12_fixed.reshape(img.shape)
Primal-dual: min_x f(Ax) + x^T z + g(x)
---------------------------------------------------------
Proximal operator (f): <class 'pyproximal.proximal.L2.L2'>
Proximal operator (g): <class 'pyproximal.proximal.L21.L21'>
Linear operator (A): <class 'pylops.basicoperators.gradient.Gradient'>
Additional vector (z): None
tau = 0.33587572106361 mu = 0.33587572106361
theta = 1.00 niter = 300
Itn x[0] f g z^x J = f + g + z^x
1 2.58711e+00 1.147e+08 1.332e+05 0.000e+00 1.148e+08
2 5.11631e+00 1.117e+08 1.386e+05 0.000e+00 1.118e+08
3 7.55886e+00 1.088e+08 1.218e+05 0.000e+00 1.090e+08
4 9.92701e+00 1.061e+08 1.117e+05 0.000e+00 1.062e+08
5 1.22573e+01 1.033e+08 1.110e+05 0.000e+00 1.035e+08
6 1.45676e+01 1.007e+08 1.145e+05 0.000e+00 1.008e+08
7 1.68645e+01 9.812e+07 1.190e+05 0.000e+00 9.824e+07
8 1.91572e+01 9.561e+07 1.244e+05 0.000e+00 9.573e+07
9 2.14549e+01 9.316e+07 1.308e+05 0.000e+00 9.329e+07
10 2.37617e+01 9.078e+07 1.378e+05 0.000e+00 9.092e+07
31 6.65923e+01 5.295e+07 2.893e+05 0.000e+00 5.324e+07
61 1.09980e+02 2.517e+07 4.559e+05 0.000e+00 2.563e+07
91 1.39128e+02 1.266e+07 5.695e+05 0.000e+00 1.323e+07
121 1.58661e+02 7.021e+06 6.458e+05 0.000e+00 7.667e+06
151 1.71745e+02 4.471e+06 6.969e+05 0.000e+00 5.168e+06
181 1.80513e+02 3.314e+06 7.312e+05 0.000e+00 4.045e+06
211 1.86389e+02 2.787e+06 7.542e+05 0.000e+00 3.542e+06
241 1.90325e+02 2.546e+06 7.696e+05 0.000e+00 3.315e+06
271 1.92963e+02 2.434e+06 7.799e+05 0.000e+00 3.214e+06
292 1.94272e+02 2.393e+06 7.851e+05 0.000e+00 3.178e+06
293 1.94326e+02 2.392e+06 7.853e+05 0.000e+00 3.177e+06
294 1.94379e+02 2.390e+06 7.855e+05 0.000e+00 3.176e+06
295 1.94431e+02 2.389e+06 7.857e+05 0.000e+00 3.175e+06
296 1.94483e+02 2.387e+06 7.859e+05 0.000e+00 3.173e+06
297 1.94534e+02 2.386e+06 7.861e+05 0.000e+00 3.172e+06
298 1.94584e+02 2.385e+06 7.863e+05 0.000e+00 3.171e+06
299 1.94633e+02 2.384e+06 7.865e+05 0.000e+00 3.170e+06
300 1.94682e+02 2.382e+06 7.867e+05 0.000e+00 3.169e+06
Total time (s) = 13.38
---------------------------------------------------------
We do the same with the adaptive algorithm
cost_ada = []
err_ada = []
iml12_ada, steps = \
pyproximal.optimization.primaldual.AdaptivePrimalDual(l2, l1iso, Gop,
tau=tau, mu=mu,
x0=np.zeros_like(img.ravel()),
niter=45, show=True, tol=0.05,
callback=lambda x: callback(x, l2, l1iso,
Gop, cost_ada,
img.ravel(),
err_ada))
iml12_ada = iml12_ada.reshape(img.shape)
Adaptive Primal-dual: min_x f(Ax) + x^T z + g(x)
---------------------------------------------------------
Proximal operator (f): <class 'pyproximal.proximal.L2.L2'>
Proximal operator (g): <class 'pyproximal.proximal.L21.L21'>
Linear operator (A): <class 'pylops.basicoperators.gradient.Gradient'>
Additional vector (z): None
tau0 = 3.358757e-01 mu0 = 3.358757e-01
alpha0 = 5.000000e-01 eta = 9.500000e-01
s = 1.000000e+00 delta = 1.500000e+00
niter = 45 tol = 5.000000e-02
Itn x[0] f g z^x J = f + g + z^x
2 2.58711e+00 1.147e+08 1.332e+05 0.000e+00 1.148e+08
3 7.57933e+00 1.089e+08 1.627e+05 0.000e+00 1.090e+08
4 1.64539e+01 9.877e+07 2.031e+05 0.000e+00 9.897e+07
5 3.10930e+01 8.306e+07 2.862e+05 0.000e+00 8.335e+07
6 5.30802e+01 6.205e+07 4.080e+05 0.000e+00 6.246e+07
7 8.22480e+01 3.911e+07 5.567e+05 0.000e+00 3.967e+07
8 1.05239e+02 2.499e+07 6.654e+05 0.000e+00 2.565e+07
9 1.23407e+02 1.629e+07 7.408e+05 0.000e+00 1.704e+07
10 1.37801e+02 1.094e+07 7.921e+05 0.000e+00 1.173e+07
13 1.63171e+02 4.733e+06 8.585e+05 0.000e+00 5.591e+06
17 1.70360e+02 3.761e+06 8.477e+05 0.000e+00 4.609e+06
21 1.75633e+02 3.311e+06 8.351e+05 0.000e+00 4.146e+06
25 1.81178e+02 2.935e+06 8.454e+05 0.000e+00 3.780e+06
29 1.85288e+02 2.699e+06 8.369e+05 0.000e+00 3.536e+06
33 1.88011e+02 2.560e+06 8.199e+05 0.000e+00 3.379e+06
37 1.90280e+02 2.474e+06 8.092e+05 0.000e+00 3.283e+06
38 1.90804e+02 2.458e+06 8.077e+05 0.000e+00 3.265e+06
39 1.91302e+02 2.444e+06 8.064e+05 0.000e+00 3.250e+06
40 1.91771e+02 2.431e+06 8.055e+05 0.000e+00 3.237e+06
41 1.92205e+02 2.420e+06 8.048e+05 0.000e+00 3.225e+06
42 1.92605e+02 2.410e+06 8.042e+05 0.000e+00 3.215e+06
43 1.92970e+02 2.402e+06 8.038e+05 0.000e+00 3.205e+06
44 1.93301e+02 2.394e+06 8.034e+05 0.000e+00 3.198e+06
45 1.93602e+02 2.387e+06 8.032e+05 0.000e+00 3.190e+06
46 1.93875e+02 2.381e+06 8.030e+05 0.000e+00 3.184e+06
Total time (s) = 2.46
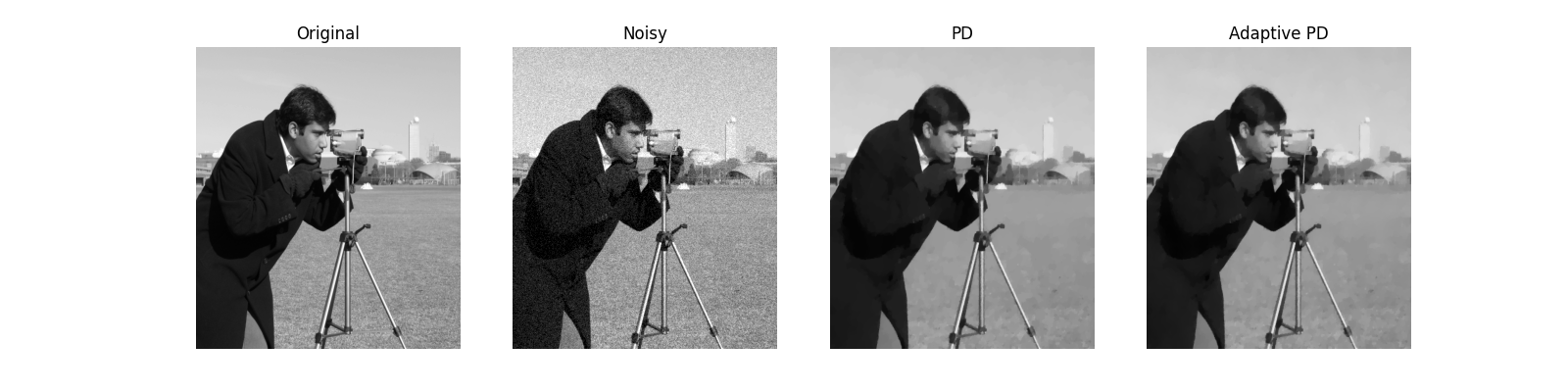
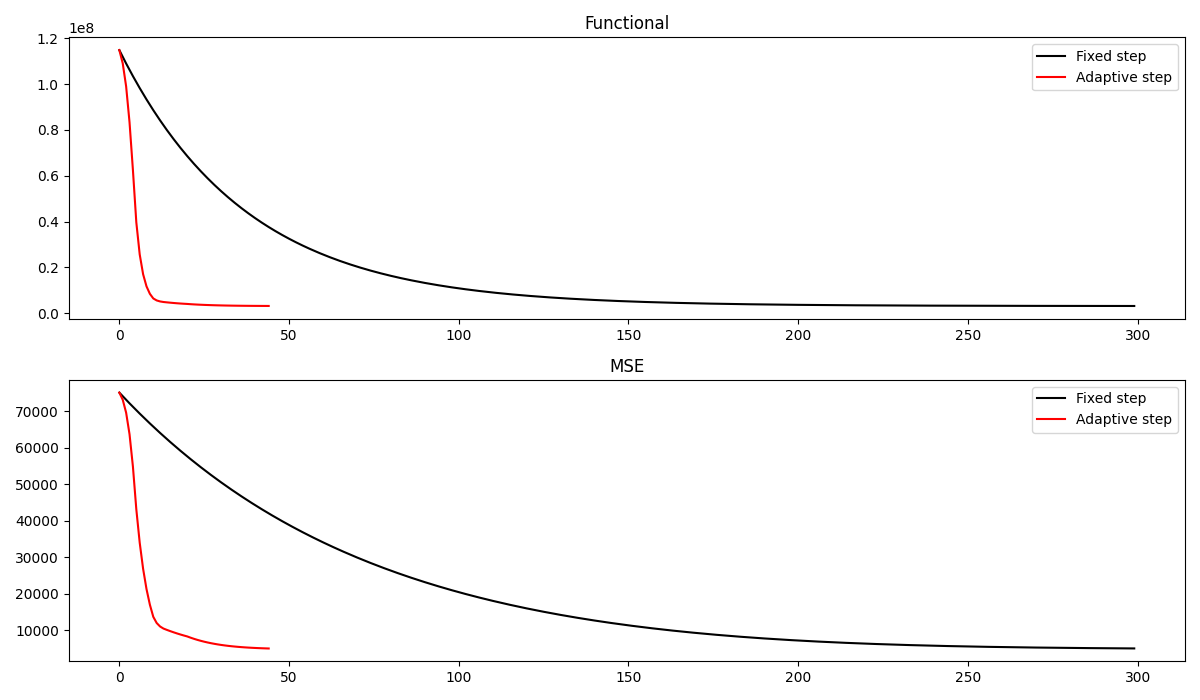
Let’s now compare the final results as well as the convergence curves of the two algorithms. We can see how the adaptive Primal-Dual produces a better estimate of the clean image in a much smaller number of iterations
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 4, figsize=(16, 4))
axs[0].imshow(img, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
axs[0].set_title('Original')
axs[0].axis('off')
axs[0].axis('tight')
axs[1].imshow(noise_img, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
axs[1].set_title('Noisy')
axs[1].axis('off')
axs[1].axis('tight')
axs[2].imshow(iml12_fixed, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
axs[2].set_title('PD')
axs[2].axis('off')
axs[2].axis('tight')
axs[3].imshow(iml12_ada, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
axs[3].set_title('Adaptive PD')
axs[3].axis('off')
axs[3].axis('tight')
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(12, 7))
axs[0].plot(cost_fixed, 'k', label='Fixed step')
axs[0].plot(cost_ada, 'r', label='Adaptive step')
axs[0].legend()
axs[0].set_title('Functional')
axs[1].plot(err_fixed, 'k', label='Fixed step')
axs[1].plot(err_ada, 'r', label='Adaptive step')
axs[1].set_title('MSE')
axs[1].legend()
plt.tight_layout()
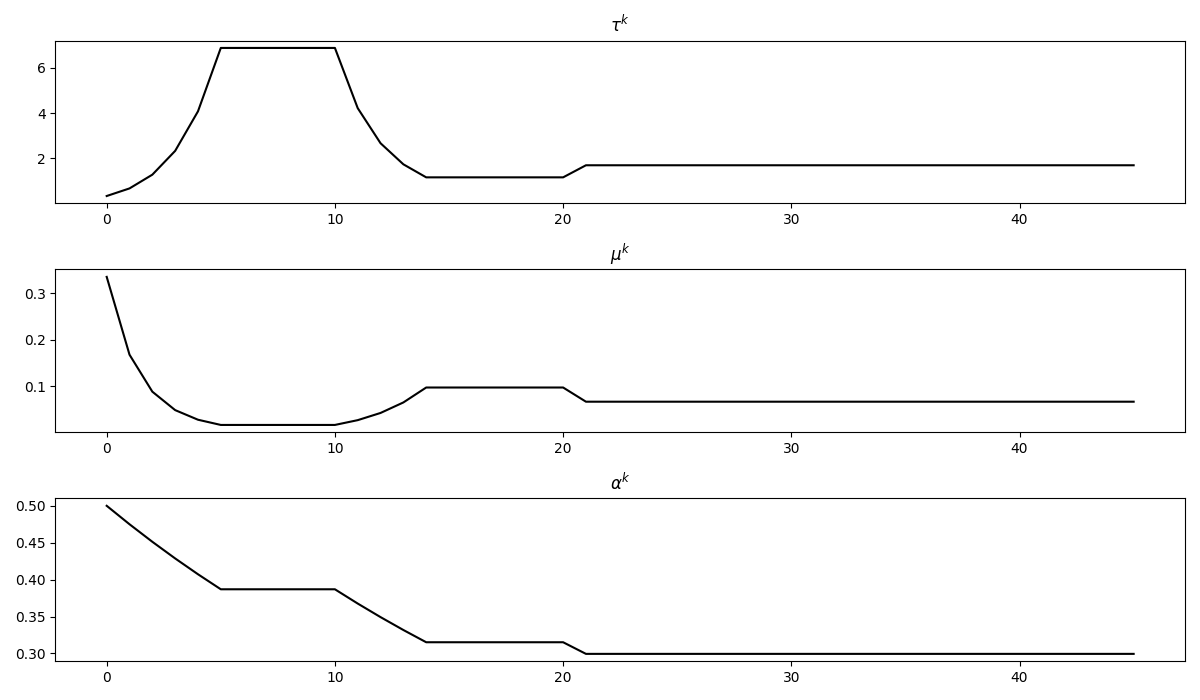
fig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(12, 7))
axs[0].plot(steps[0], 'k')
axs[0].set_title(r'$\tau^k$')
axs[1].plot(steps[1], 'k')
axs[1].set_title(r'$\mu^k$')
axs[2].plot(steps[2], 'k')
axs[2].set_title(r'$\alpha^k$')
plt.tight_layout();
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 17.022 seconds)