pyproximal.SCAD#
- class pyproximal.SCAD(sigma, a=3.7)[source]#
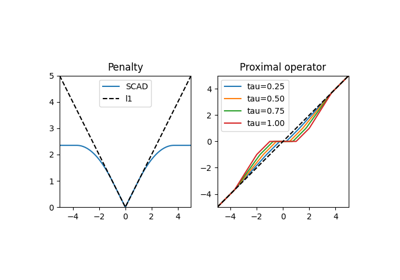
Smoothly clipped absolute deviation (SCAD) penalty.
The SCAD penalty is a concave function and is defined as
\[\begin{split}\mathrm{SCAD}_{\sigma, a}(\mathbf{x}) = \begin{cases} \sigma x_i, & |x_i| \leq \sigma \\ \frac{-x_i^2 + 2 a \sigma - \sigma^2}{2 (a - 1)}, & \sigma < |x_i| \leq a\sigma \\ \frac{(a + 1)\sigma^2}{2}, & |x_i| > a\sigma \end{cases}\end{split}\]- Parameters
Notes
The SCAD penalty is continuous and differentiable and does not suffer from biasedness as the \(\ell_1\)-norm, nor is discontinuous as the hard thresholding penalty. Thus, it fuses the most favourable properties of both penalties.
The proximal operator is given by
\[\begin{split}\prox_{\tau \mathrm{SCAD}_{\sigma, a}(\cdot)}(\mathbf{x}) = \begin{cases} \sgn(x_i)\max(0, |x_i| - \sigma), & |x_i| \leq \frac{\sigma(a - 1 - \tau + a\tau)}{a - 1} \\ \frac{(a-1)x_i - \sgn(x_i)a\tau\sigma}{a-1-\tau}, & \frac{\sigma(a - 1 - \tau + a\tau)}{a - 1} < |x_i| \leq a\sigma \\ x_i, & |x_i| > a\sigma \end{cases}\end{split}\]- 1(1,2)
Fan, J. and Li, R. “Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 96(456):1348–1360, 2001
Methods
__init__(sigma[, a])affine_addition(v)Affine addition
chain(g)Chain
elementwise(x)grad(x)Compute gradient
postcomposition(sigma)Postcomposition
precomposition(a, b)Precomposition
prox(**kwargs)proxdual(**kwargs)